Trochanteric Bursectomy
What is Trochanteric Bursectomy?
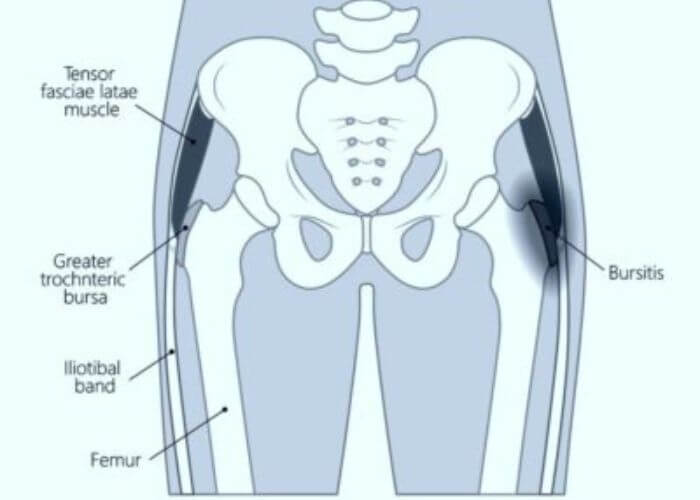
- A surgical procedure to treat chronic trochanteric bursitis, a painful condition affecting the outer hip.
- It involves removing the inflamed bursa, a fluid-filled sac that cushions the muscles and tendons around the hip joint.
When is Surgery Necessary?
- Chronic Bursitis: When conservative treatments (rest, ice, physical therapy, medications) have failed to provide adequate relief from persistent and worsening symptoms of trochanteric bursitis.
- Symptoms: These may include:
- Severe, persistent hip pain: Often localized to the outer side of the hip.
- Pain with activity: Especially activities like walking, climbing stairs, or lying on the affected side.
- Limited range of motion
Surgical Procedure
- Minimally Invasive: Typically performed as a minimally invasive procedure using arthroscopic techniques.
- Small Incisions: Small incisions are made near the hip.
- Arthroscope: A small camera (arthroscope) is inserted to visualize the area.
- Removal of Bursa: Specialized instruments are used to remove the inflamed bursa.
- Release of Tight Tissues: The surgeon may also release any tight or irritated tissues around the hip, such as the iliotibial band (IT band).
Recovery
- Short Hospital Stay: Usually an outpatient procedure, but may require a short hospital stay.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is crucial for regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the hip.
- Return to Activity: A gradual return to normal activities is recommended, with full recovery typically taking several weeks or months.
Important Considerations
- Minimally Invasive: Arthroscopic techniques generally result in less pain, scarring, and faster recovery compared to open surgery.
- Success Rates: Trochanteric bursectomy is generally successful in relieving pain and improving function.
- Risks: As with any surgery, there are potential risks, such as infection, nerve damage, and stiffness.
Disclaimer
This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.