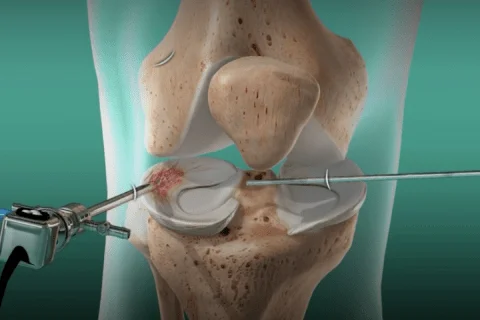
Synovectomy
What is Synovectomy?
- Synovectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing or reducing the synovial membrane, which lines the joints.
- The synovial membrane produces synovial fluid, which lubricates and nourishes the joint.
When is Surgery Necessary?
Synovitis: Synovectomy is primarily performed to treat synovitis, which is inflammation of the synovial membrane.
Conditions: Synovitis can occur in various conditions, including:
Rheumatoid arthritis: A chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints.
Other forms of arthritis: Such as psoriatic arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Infections: Infections within the joint can also cause inflammation of the synovium.
Surgical Procedure
- Arthroscopic Synovectomy:
- The most common approach.
- Involves small incisions around the joint and the use of an arthroscope (a small camera) to visualize the joint interior.
- Specialized instruments are used to remove the inflamed synovial tissue.
- Open Synovectomy:
- May be necessary in some cases, such as when extensive removal of synovium is required.
- Involves a larger incision around the joint.
Recovery
- Short Hospital Stay: Usually an outpatient procedure, but may require a short hospital stay.
- Immobilization: The joint may be immobilized with a splint or brace for a short period.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is essential to regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Return to Activity: Gradual return to normal activities is recommended, with full recovery typically taking several weeks or months.
Important Considerations
- May Not Cure the Underlying Condition: Synovectomy can help alleviate pain and improve joint function, but it does not cure the underlying condition (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis).
- May Need to be Repeated: In some cases, synovectomy may need to be repeated if the inflammation returns.
- Risks: As with any surgery, there are potential risks, such as infection, bleeding, and stiffness.
Disclaimer
This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.