Patellar Realignment (Patellar Tendon Surgery)
What is Patellar Realignment (Patellar Tendon Surgery)?
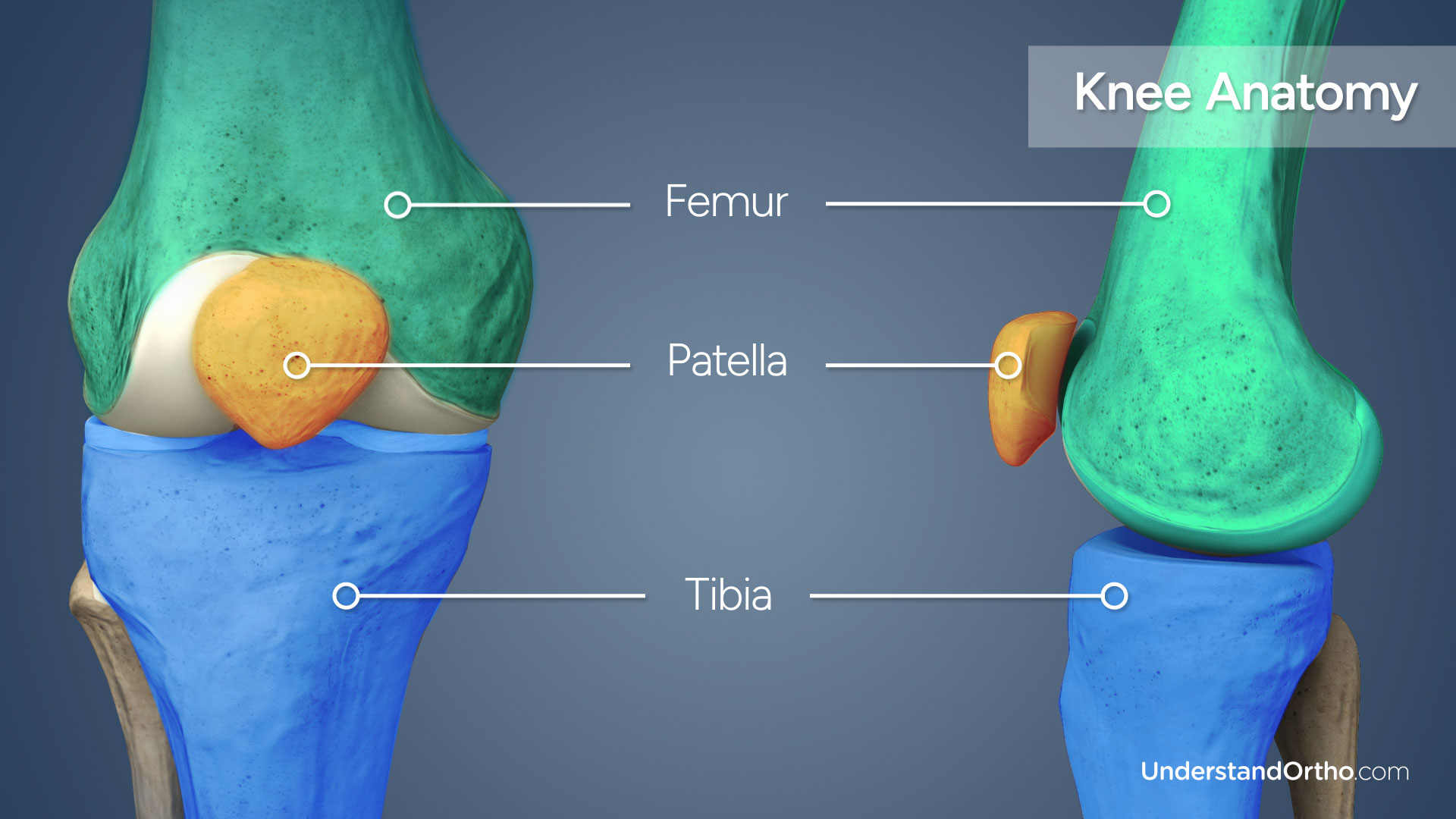
- Patellar realignment surgery is a procedure to correct problems with the tracking or alignment of the kneecap (patella).
- The kneecap is supposed to glide smoothly within a groove on the femur (thighbone) during knee movement.
- When the kneecap tracks abnormally, it can cause:
- Pain
- Swelling
- "Clicking" or "grinding" noises
- Difficulty with knee movement
When is Surgery Necessary?
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: When conservative treatments (physical therapy, bracing, medications) fail to provide adequate relief from persistent patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFP), a condition characterized by pain around or behind the kneecap.
- Patellar Instability: When the kneecap frequently dislocates or subluxes (partially dislocates) from its normal groove.
Surgical Procedure
- Various Techniques: The specific procedure depends on the underlying cause of the patellar malalignment. Common techniques include:
- Lateral Release: Releasing tight ligaments on the outer side of the knee to improve kneecap tracking.
- Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Reconstruction: Repairing or reconstructing the MPFL, a ligament that helps stabilize the kneecap.
- Tibial Tuberosity Transfer: Moving the tibial tuberosity (the bony bump on the shinbone where the patellar tendon attaches) slightly inward to improve kneecap alignment.
Recovery
- Immobilization: The knee may be immobilized with a brace or splint for a short period.
- Physical Therapy: Extensive physical therapy is crucial for regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion. This may involve exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve balance, and gradually return to normal activities.
- Return to Activity: A gradual return to normal activities and sports is recommended, with full recovery often taking several months.
Important Considerations
- Success Rates: Success rates vary depending on the underlying cause of the patellar malalignment and the specific surgical technique used.
- Risks: As with any surgery, there are potential risks, such as infection, nerve damage, and stiffness.
Disclaimer
This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.