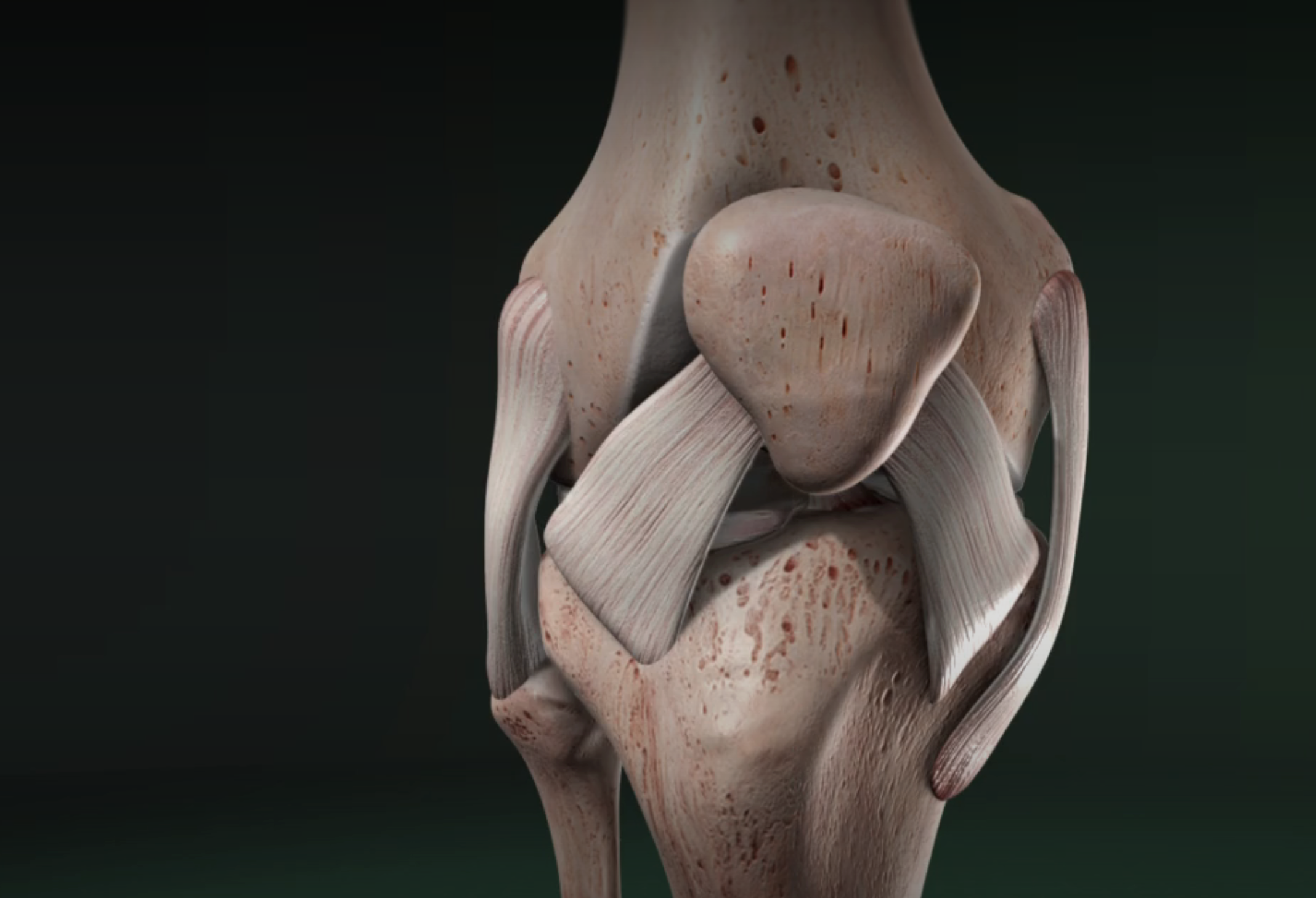
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Reconstruction
What is Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Reconstruction?
A surgical procedure to repair a torn Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) in the knee.
The PCL is a crucial ligament that connects your shinbone (tibia) to your thighbone (femur), providing stability to the knee joint by preventing the shinbone from sliding too far backward.
When is Surgery Necessary?
Complete PCL Tear: When the PCL is completely torn, surgical reconstruction is often recommended, especially in active individuals.
Significant Instability: If the knee joint feels unstable or gives way frequently after a PCL tear.
Surgical Procedure
- Arthroscopic Technique: PCL reconstruction is typically performed arthroscopically, using small incisions and a tiny camera to visualize the inside of the knee.
- Graft Selection: A graft is used to replace the torn PCL. Common graft sources include:
- Hamstring tendons: Taken from the back of the thigh.
- Quadriceps tendon: Taken from the front of the thigh.
- Allograft: Tissue from a deceased donor.
- Graft Placement: The graft is secured within the knee joint in the same position as the original PCL.
Recovery
- Immobilization: The knee may be immobilized with a brace for a short period.
- Physical Therapy: Extensive physical therapy is crucial for regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion. This may involve exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve balance, and gradually return to normal activities.
- Return to Activity: A gradual return to normal activities and sports is recommended, with full recovery often taking several months.
Important Considerations
- Success Rates: PCL reconstruction surgery generally has a high success rate in restoring stability to the knee.
- Risks: As with any surgery, there are potential risks, such as infection, nerve damage, and stiffness.
- Re-rupture: There is a small risk of the reconstructed ligament re-rupturing.
Disclaimer
This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.